Introduction
Pharmaceutical companies have been among the healthcare industry's top achievers recently due to an ageing population, rising healthcare costs, and the continuous development of new, highly valued pharmaceuticals. Investors in top-tier pharmaceutical companies can choose from a wide variety of publicly traded corporations. For informed choices, investors should consider the best financial ratios for analyzing and evaluating the equity of pharmaceutical companies.
Financial Metrics and Drug Companies
The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by significant expenses associated with research and development (R&''D) and a long time lag between the discovery of a new product and its introduction to the market. When a new drug is released into the market, the corporation responsible for it will set the price of the drug to repay its investment in the shortest amount of time possible. The ratio of a pharmaceutical company's total debt to its annual profits is an essential indicator of the health of the company's finances.
The Ratio of Return on Investment in Research Funds
A ratio demonstrating a company's financial return from its research and development spending is crucial for examining pharmaceutical businesses. The pharmaceutical industry's research and development costs are so high. The return on research capital ratio is the standard method for determining how successfully a company can turn its R&''D spending into a profit. This evaluation is performed on the company (RORC). The remaining sum can be calculated by dividing the current year's gross profit by the amount spent on research and development in the previous year. By analyzing the Return on R&''D Investment, investors can gain insight into the efficiency with which R&''D expenditures translate into profits (RORC).
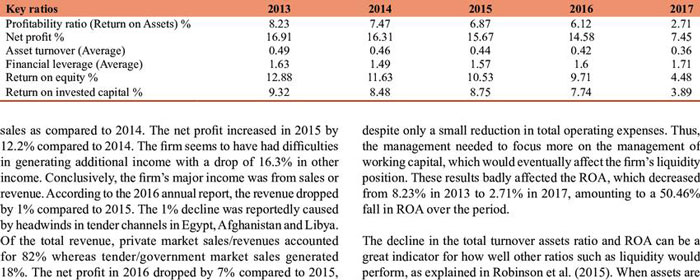
Key Performance Indicators
After a pharmaceutical company has released a medication onto the market, the following essential steps are mass manufacture and sales of the drug. As a consequence of this, shareholders should focus their attention intently on the operating margin as well as the net margin. Examining a company's operating margin (calculated by subtracting revenue from production costs) and net margin is one method for determining how adept it is at decreasing costs (revenue minus operating costs and other miscellaneous expenses).
Ratios for Measures of Financial Flexibility and Debt Service
For pharmaceutical businesses to be able to finance the massive amounts of capital spending required for R&''D, they need to have sufficient cash on hand in addition to an effective plan for managing the enormous levels of debt they often carry. The quick ratio is a measurement of a firm's short-term liquidity, and it reveals whether or not the company has sufficient cash on hand to continue operations. To calculate it, start by deducting inventory from current assets. Then, divide the resulting number by current liabilities and round the result to the nearest whole number.
As a measure of a firm's ability to pay its short-term debts, the quick ratio contrasts the number of liquid assets the company has at its disposal with its short-term debt. The debt ratio is a metric of leverage that may be used to determine how much of an organization's assets are funded by debt. To determine the debt-to-asset ratio, divide the total amount of debt by the value of all the help. Businesses in the pharmaceutical industry can only prosper and grow if they can effectively manage their existing debt.
The Rate of Return on Investment
One of the most important questions for investors is how profitable a company is about the capital they have invested. Return on equity (ROE) is a widely used metric to assess how well a firm is doing financially by returning cash to its owners. Considering the enormous sums of money needed to bring new pharmaceuticals to market, return on equity (ROE) is a crucial metric for evaluating pharmaceutical companies.
Therefore, management efficiency and the company's long-term profitability can be assessed by analyzing how they spend stockholders' money. Return on equity can be determined by dividing net income by shareholders' equity (ROE). Even if a company has a higher-than-average return on equity (ROE), investors shouldn't trust it if it has used excessive financial leverage to get there. Therefore, evaluating a pharmaceutical company's debt and liquidity is essential.
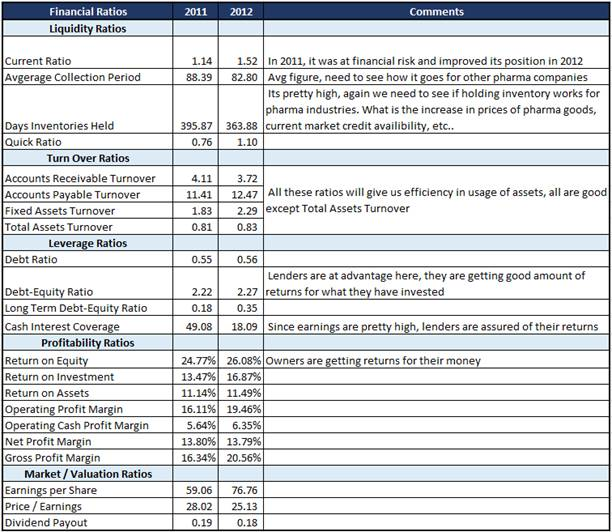
Conclusion
The percentage of businesses open to public investment and involvement has risen significantly alongside the expansion of global trade, commerce, and manufacturing production. When a country is trying to industrialize, the pharmaceutical industry plays a crucial role. However, industry-wide net earnings have been on the decline for a while. The research set out to determine what factors contribute to the success or failure of this sector's economy.



